Written By: Kiat Yi
MB0902
093712T
MB0902
093712T
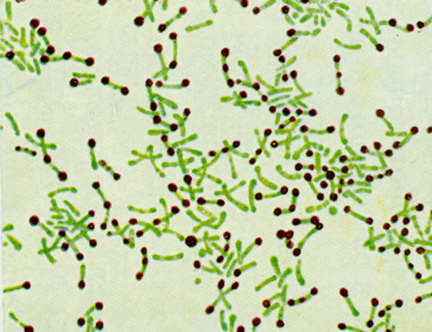
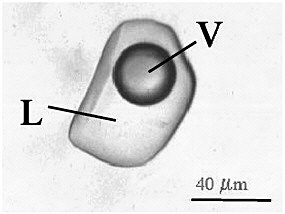
Cell Inclusions are aggregates of various compounds that are normally involved in storing energy reserves or building blocks for the cell. That means that they are made up of a combination of cell compounds, mainly proteins, and besides being the building blocks of the cell, they also store the cell’s excess energy for future use.
Cell inclusions are small, non-living intracellular (that means “inside the cell”) particles, usually represented as a form of stored food, and are not immediately vital to life processes. They also typically represent sites of viral multiplication in a bacterium or a eukaryotic cell and usually consist of viral capsid proteins (the protein shell of a virus).
Some examples of inclusions include:
- metachromatic granules
- polysaccharide granules
- lipid inclusions
- sulfur granules
- carboxysomes
- gas vacuoles
Reference Link: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inclusion_bodies

0 comments:
Post a Comment